- 0% APR Financing Available for up to 3 months*
-
Lifetime Upgrade
We are committed to serving our customers not only for a sale, but during a lifetime.
More Info
-
Jewelry Warranty
For your peace of mind, all B2C Jewels items are covered by a 1-year warranty.
More Info
-
Price Match Gaurantee
B2C Jewels is committed to offer the best price available on certified diamonds.
More Info
Education
Your Guide to Become a Jewelry Expert
Certificate
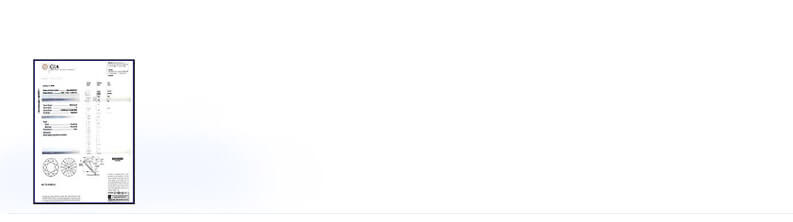
Many gemological laboratories give a report of their evaluation of a diamond that influences the price of the diamond. Certificates are minute details and characteristics of a diamond that are not visible to the naked eye. For a buyer, diamond certificate is an assurance that the product bought is genuine and is worth the amount paid.
Sample GIA Diamond Grading Report View
Why need a Diamond Certificate?
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has various grading scales to judge the purity of a diamond. They are:
- A certificate assures a diamond buyer of the quality and authenticity of the diamond.
- As most diamond buyers are not experts, a certificate allows an objective comparison.
- In addition should you resell your gem, the certificate will provide the stamp of authenticity you'll need to get a fair price.
Which Gemological Labs are reliable?
1. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA):
GIA is the most reputed and reliable laboratory for gem evaluation as it has developed the first internationally accepted Diamond Grading System and set the standard for diamond quality documentation around the world. The GIA Gem Trade Laboratory issues these reports on a majority of high quality diamonds over one carat in size.
Details in a GIA Diamond Certificate:
- Date: Located at the top most left corner of the report, it shows the date on which the Diamond was examined and issued by GIA.
- GIA Report Number: Unique GIA identification number.
- Laser Inscription Registry: At the request of the customer, the diamond is micro laser inscribed with its unique GIA Report Number.
- Shape And Cutting Style: Description of the outline of the diamond (shape) and the pattern of the facet arrangement (cutting style).
- Measurements: The dimensions of the diamond listed as minimum diameter - maximum diameter x depth for round diamonds and length x width x depth for fancy shape diamonds.
- Carat Weight: The weight of the diamond given in carats
- Color Grade: The assessment of absence of color from colorless to light yellow or brown when compared to GIA Master Color Comparison Diamonds.
- Clarity Grade:The assessment of inclusions (internal characteristics) and blemishes (external characteristics) visible under 10x magnifiers.
- Clarity Characteristics: The description of any internal and/or external characteristics, if present.
- Cut Grade: A grading for the cut of diamond ranging from excellent to fair.
- Polish: The overall condition or smoothness of the diamond's surface.
- Symmetry: Exactness of the diamond's outline and the shape, placement and alignment of its facets.
- Fluorescence: The strength and the color of the diamond when viewed under long-wave ultra violet light.
- Comments: The additional identifying characteristics or features that are otherwise not represented on the report.
- GIA Color and Clarity Scales: The grading scale graphics of GIA Clarity and Color with the relative positions of color and inclusions in the GIA Diamond Grading System.
- Proportion Diagram: A Graphical profile representation with the diamond's actual proportions.
- Security Features: A suite of security components including a hologram, security screen and microprint lines in addition to several other proprietary security features to ensure integrity.
2. American Gem Society (AGS):
AGS laboratories serve an international clientele of retail jewelers, wholesale suppliers, diamond cutters and manufacturers. AGS' Diamond Quality Document or DQD provides information on all 4 C's of diamond grading. Ratings are given on a scale of 0 to 10.
- AGS Clarity Grade: This scale ranges from 0 to 10, 0 being the rarest and most desirable and 10 the least desirable. An AGS Grade of 0, with no comments about the finish of the diamond in the comments section of the document, is equivalent to the GIA Grade of Flawless. An AGS Grade of 0 with comment(s) referring to the finish or surface characteristics is equivalent to the GIA Grade of Internally Flawless.
- AGS Color Grade: The AGS Color Scale is based on the original colorimeter invented by Robert M. Shipley Jr. The old AGS scale had only eleven color grades 0 to10, which was then updated with point increments. This update provided three things: more accuracy, more grades (21 instead of 11) and exact cross-reference to the GIA letter scale.
- AGS Plot: The plot, including the crown and pavilion views, is printed directly on the DQD. For Round diamonds, the AGS laboratories are able to print the crown view with the accurate table diameter percentage.
3. International Gemological Institute (IGI):
Over 250 staff members at IGI issue over 400,000 gem reports annually. IGI has three distinct products: Diamond Report, Identification Report and Information Appraisal Report.
4. European Gemological Laboratory (EGL):
EGL has defined criteria and standard procedures for accuracy and consistency in its Diamond Certificate and Diamond Consultation. EGL Certificates are recognized worldwide. Their main clients are diamond wholesalers, dealers, manufacturers, and craftsmen.






